Weekly Reading List: June 2, 2025
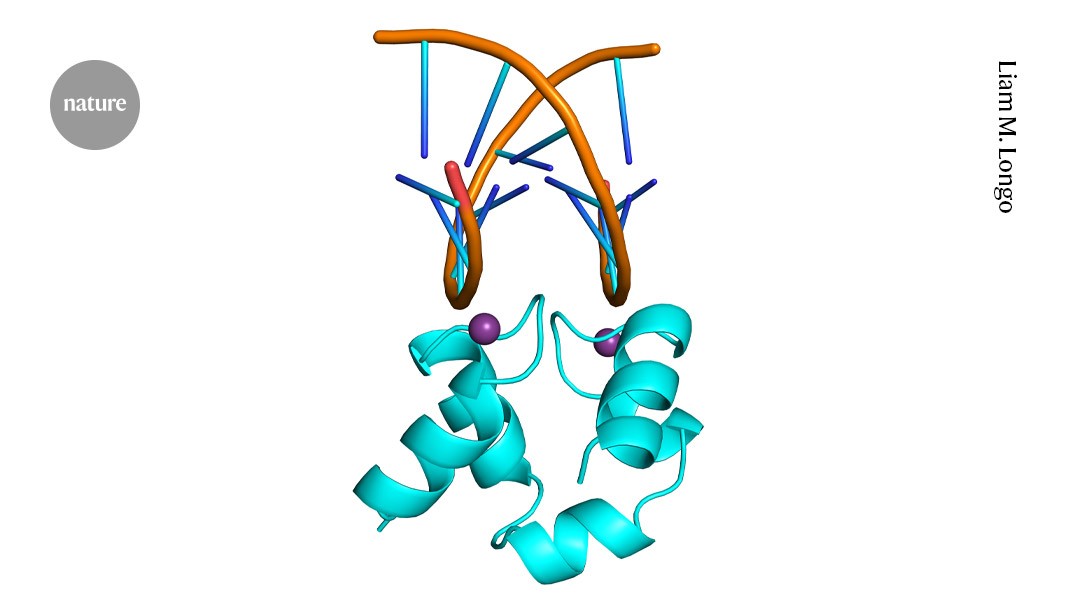
Rare ‘ambidextrous’ protein breaks rules of handedness
Most proteins are left-handed, but scientists have found an ancient molecule that works in both mirror-image forms.
European Sperm Donor Passes on Cancer Predisposition Variant to at Least 23 Children
A donor to a European
sperm bank has transmitted a likely pathogenic variant for Li-Fraumeni
syndrome, a genetic condition that predisposes carriers to a variety of
cancers, to almost two dozen children he fathered, of whom 10 have
developed cancer so far.
At ASCO 2025, attendees see reason for hope, despite worries
Like a Las Vegas buffet, ASCO offers a diverse bounty of clinical data.

Prioritizing disease-associated missense variants with chemoproteomic-detected amino acids
Missense variants are
the most common type of protein-altering genetic variation. Due to their
wide-ranging potential functional consequences, missense variants are
challenging to interpret and, as a result, are often classified as
unknown pathogenicity or as variants of uncertain significance (VUSs).
Genomic-based predictive tools have made significant inroads into the
challenge of accurately pinpointing functional missense variants by
providing genome-wide assessments of deleteriousness or potential
pathogenicity. Complementary to these tools, here we provide an initial
study into the utility of harnessing protein-based measures of amino
acid reactivity to delineate functionally significant missense variants.
These reactivity measurements, which are generated using mass
spectrometry-based chemoproteomic methods, have already proved capable
of pinpointing functional sites on proteins, which provide the added
value of delineating potential sites suitable for drug-development
efforts.
Epigenome-wide DNA methylation association study of CHIP provides insight into perturbed gene regulation - Nature Communications
In
CHIP, somatic mutations in a hematopoietic stem cell lead to a clonal
subpopulation of blood cells. Here, the authors perform a CHIP meta-EWAS
to establish its epigenetic features and age-related outcomes.
Accurate HBA and SMN genotyping within an integrated NGS workflow: A step toward accessible carrier screening
Here,
we present updated versions of SMN and HBA targeted callers, released
in DRAGEN v4.4, as well as a spike-in panel that can be used to
supplement the Illumina DNA Prep with Exome 2.5 Enrichment panel to
allow for accurate HBA and SMN genotyping on Illumina exomes.
Hologic Shares Spike 15 Percent on Reports of $16B Offer to Go Private
Shares of Hologic
jumped 15 percent on Tuesday following a report that the company had
rejected an offer totaling more than $16 billion to take it private.
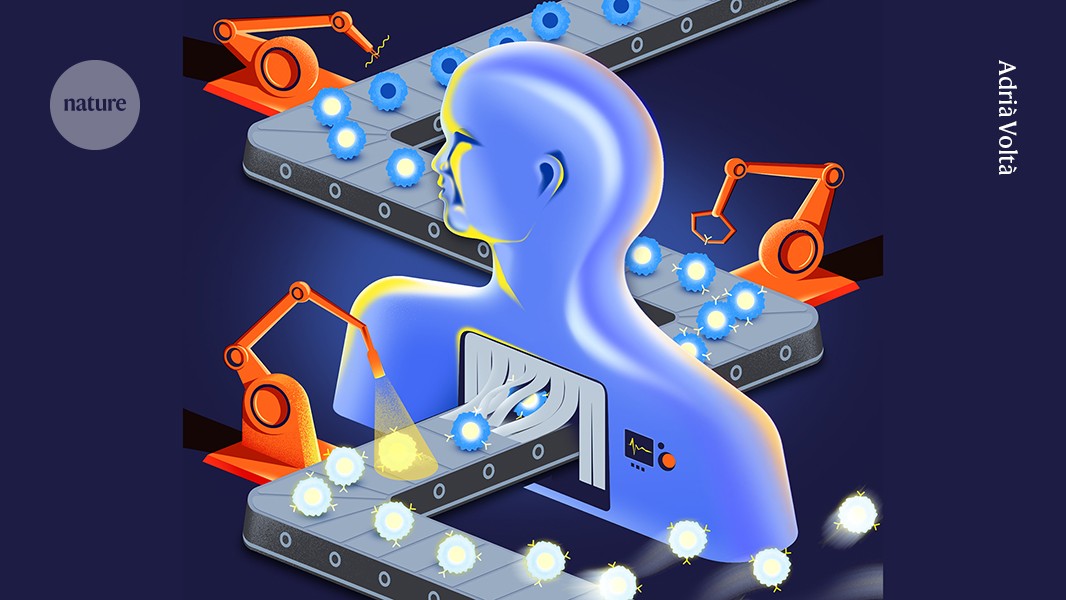
Cancer-fighting immune cells could soon be engineered inside our bodies
Manufacturing
CAR T cells in the laboratory is expensive and time-consuming. An in
vivo approach could get the powerful therapy to more people.
Drug-induced liver injuries rise in the U.S. as supplements grow in popularity: What to know
Most people who take dietary or herbal supplements do so on their own, not under a doctor’s advice.

Former FDA commissioner: ‘Cost-cutting’ may undo one of Trump’s best drug pricing achievements
The
recent dismissal of 13 FDA review staff eliminated precisely the kind
of government spending that delivered the most bang for the taxpayers’
buck, writes former FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb.

The ‘pivot penalty’: scientists get cited less after switching fields, analysis finds
Massive study of nearly 26 million research papers measures the consequences of striking out in another research area.

Caris Life Sciences Files for IPO
Caris Life Sciences
said late Friday that it has filed a registration statement with the US
Securities and Exchange Commission for an initial public offering.
Illumina unveils PromoterAI, a groundbreaking algorithm to accelerate insights for rare disease diagnosis

Expansion in situ genome sequencing links nuclear abnormalities to aberrant chromatin regulation
Microscopy and genomics
are used to characterize cell function, but approaches to connect the
two types of information are lacking, particularly at subnuclear
resolution. Here, we describe expansion in situ genome sequencing
(ExIGS), a technology that enables sequencing of genomic DNA and
superresolution localization of nuclear proteins in single cells.
Applying ExIGS to progeria-derived fibroblasts revealed that lamin
abnormalities are linked to hotspots of aberrant chromatin regulation
that may erode cell identity. Lamin was found to generally repress
transcription, suggesting variation in nuclear morphology may affect
gene regulation across tissues and aged cells. These results demonstrate
that ExIGS may serve as a generalizable platform to link nuclear
abnormalities to gene regulation, offering insights into disease
mechanisms.
Patient dies in trial of Rocket gene therapy for heart condition
The
FDA has placed a clinical hold on the study while Rocket works with
trial monitors and experts to investigate the cause of the patient’s
death.
udicial Invalidation of the FDA’s Laboratory-Developed Test Rule — Legal and Public Health Consequences
Recently, a federal
judge struck down an FDA rule on laboratory-developed tests. If this
invalidation stands, it will have consequences for clinical care and the
FDA’s authority over medical devices.
Immunotherapy drug doubles cancer survival in breakthrough trial
An international study found immunotherapy before surgery could give patients extra years of life.

Scientists have lost their jobs or grants in US cuts. Foreign universities want to hire them
As
the Trump administration cut billions of dollars in federal funding to
scientific research, thousands of scientists in the U.S. lost their jobs
or grants.

Beyond Genes: Human Exposome Project to Tackle External Drivers of Disease
The Human Genome
Project began more than 30 years ago, creating a reference map that has
since transformed the understanding of how genes contribute to health
and disease. Now, the Human Exposome Project seeks to uncover how the
complete range of environmental factors shapes health.
Étienne-Émile Baulieu, French scientist who invented abortion pill, dies aged 98
Doctor whose discovery helped create mifepristone was ‘guided by his commitment to progress made possible by science’

25 million cavities and $9.8 billion: Study estimates the costs of removing fluoride from water
Researchers
estimated 7.5% more U.S. children would get cavities, affecting 25.4
million additional teeth, if fluoridation were banned nationwide

Black Death bacterium has become less lethal after genetic tweak
Reducing the number of copies of one gene in the pathogen could also make it more transmissible.

The organ farm
Gene-edited pig kidneys are finally moving the long-stymied field of xenotransplantation forward















