Weekly Reading List: June, 23 2025
Gene therapy faces fresh uncertainty as two more top FDA officials depart
The
reported dismissal of high-ranking CBER officials Nicole Verdun and
Rachael Anatol resurfaced lingering concerns about how gene therapies
will be regulated under new FDA leadership.

FDA blocks new clinical trials that ship cells from US to China
The
FDA has stopped new | The FDA has stopped new clinical trials that
export American citizens’ living cells from the U.S. to “China and other
hostile countries for genetic engineering and subsequent infusion” back
into American patients.

Accurate and scalable exchange-correlation with deep learning
Density
Functional Theory (DFT) is the most widely used electronic structure
method for predicting the properties of molecules and materials.
Although DFT is, in principle, an exact reformulation of the Schrödinger
equation, practical applications rely on approximations to the unknown
exchange-correlation (XC) functional. Most existing XC functionals are
constructed using a limited set of increasingly complex, hand-crafted
features that improve accuracy at the expense of computational
efficiency. Yet, no current approximation achieves the accuracy and
generality for predictive modeling of laboratory experiments at chemical
accuracy -- typically defined as errors below 1 kcal/mol. In this work,
we present Skala, a modern deep learning-based XC functional that
bypasses expensive hand-designed features by learning representations
directly from data. Skala achieves chemical accuracy for atomization
energies of small molecules while retaining the computational efficiency
typical of semi-local DFT. This performance is enabled by training on
an unprecedented volume of high-accuracy reference data generated using
computationally intensive wavefunction-based methods. Notably, Skala
systematically improves with additional training data covering diverse
chemistry. By incorporating a modest amount of additional high-accuracy
data tailored to chemistry beyond atomization energies, Skala achieves
accuracy competitive with the best-performing hybrid functionals across
general main group chemistry, at the cost of semi-local DFT. As the
training dataset continues to expand, Skala is poised to further enhance
the predictive power of first-principles simulations.

Chairs of 36 US chemistry departments call to restore funding
Open letter in <i>Science</i> says federal policy decisions ‘threaten the strength of the US research enterprise’

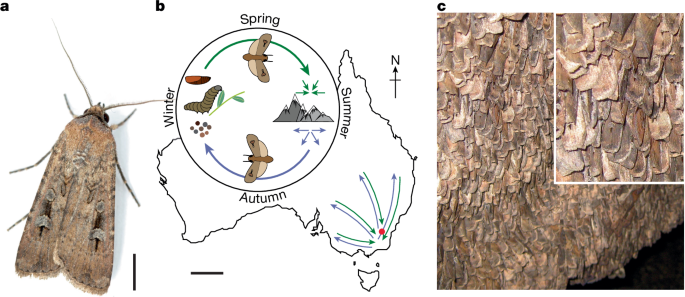
Bogong moths use a stellar compass for long-distance navigation at night - Nature
Every spring, Bogong moths use the starry night sky as a compass to navigate up to 1,000 km towards their alpine migratory goal.
Second DMD Patient Dies After Treatment with Sarepta Gene Therapy
Sarepta
halts Elevidys shipments for non-ambulatory DMD patients after a second
patient death in three months post gene therapy treatment.

Congress shows first signs of resisting Trump’s plans to slash science budgets
House panel rejects cuts to agricultural research, and Senators express doubts about cuts to NIH and forest research
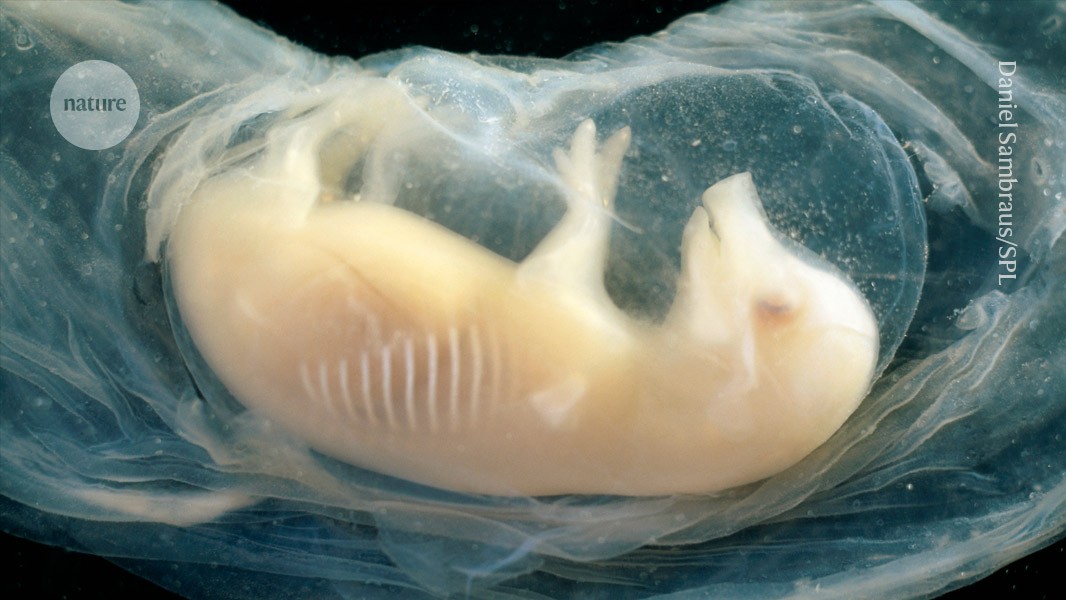
Tiny human hearts grown in pig embryos for the first time
The hearts started to beat in the pig–human hybrids, which survived for 21 days.
Judge deems Trump’s cuts to National Institutes of Health illegal
The
federal judge said the NIH violated federal law by arbitrarily
canceling more than $1 billion in research grants because of their
perceived connection to DEI initiatives.

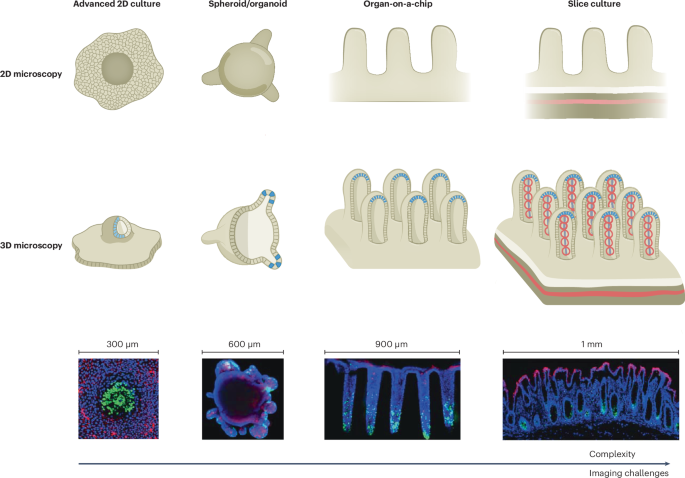
Imaging 3D cell cultures with optical microscopy - Nature Methods
This
Review discusses current 2D and 3D microscopy methods for imaging
three-dimensional cell cultures and emerging strategies to address key
challenges.
STAMP: Single-cell transcriptomics analysis and multimodal profiling through imaging
Single-cell RNA
sequencing has revolutionized our understanding of cellular diversity
but remains constrained by scalability, high costs, and the destruction
of cells during analysis. To overcome these challenges, we developed
STAMP (single-cell transcriptomics analysis and multimodal profiling), a
highly scalable approach for the profiling of single cells. By
leveraging transcriptomics and proteomics imaging platforms, STAMP
eliminates sequencing costs, enabling cost-efficient single-cell
genomics of millions of cells. Immobilizing (stamping) cells in
suspension onto imaging slides, STAMP supports multimodal (RNA, protein,
and H&E) profiling, while retaining cellular structure and
morphology.
Early Microbial Life: Our Past, Present, and Future
The
Academy report, funded by a grant from the Gordon and Betty Moore
Foundation, examines the origins and trajectory of early microbial life
to inform and inspire future research.

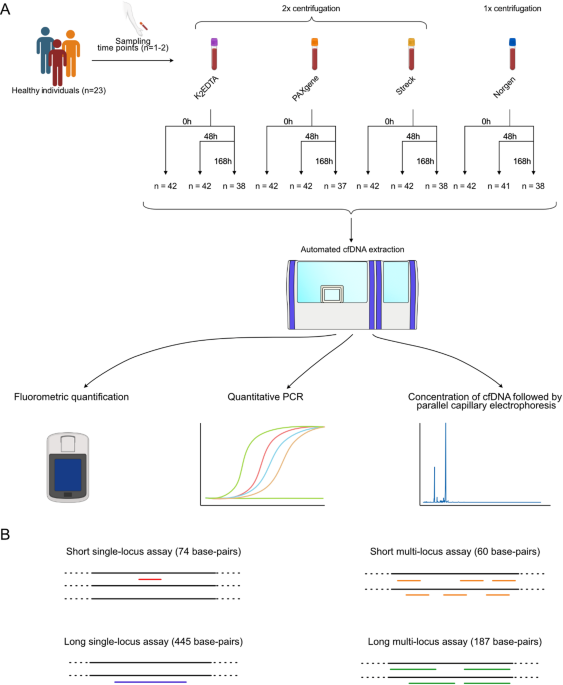
Evaluation of automatic cell free DNA extraction metrics using different blood collection tubes - Scientific Reports
Scientific Reports - Evaluation of automatic cell free DNA extraction metrics using different blood collection tubes
Xaira Therapeutics Releases Largest Perturb-Seq Dataset to Power the Virtual Cell
The
AI unicorn’s Perturb-seq atlas is publicly available and detects
dose-dependent genetic effects to enhance predictive power for drug
discovery.

‘Super-healing’ animals inspire human treatments
Studies of the regenerative powers of worms, zebrafish and lizards suggest ways to improve recovery in people.

Happy birthday Jaws! How the movie changed shark science
Half a century after its cinematic release, Jaws is still shaping how we view — and protect — the ocean’s top predators.

Roche Gives SBX Updates - and a Name!
Last
week I double-dipped on conferences, going from London Calling to
European Society for Human Genetics (ESHG) in Milan. I have a raft o…

All babies in England to get DNA test to assess risk of diseases within 10 years
Newborns will have whole genome sequencing to enable personalised healthcare that predicts and prevents illness

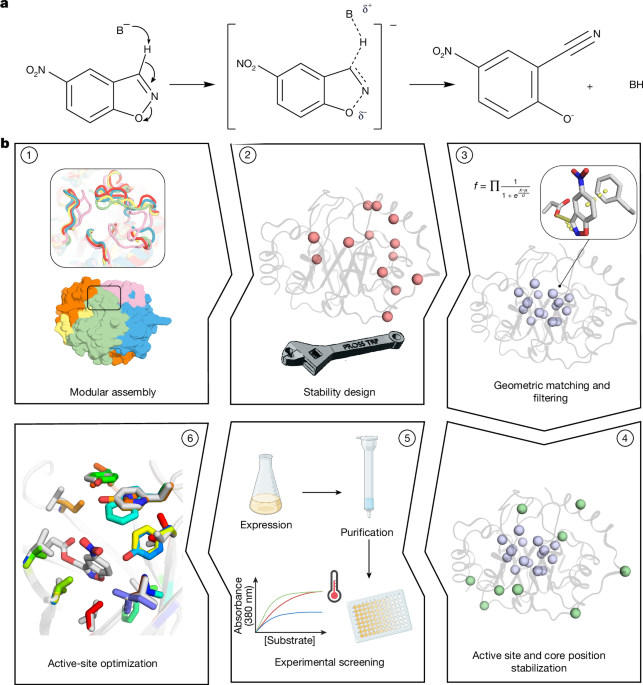
Complete computational design of high-efficiency Kemp elimination enzymes - Nature
We
present a computational approach to the design of high-efficiency
enzymes with catalytic parameters comparable to natural enzymes,
enabling programming of stable, high-efficiency, new-to-nature Kemp
elimination enzymes through minimal experimental effort.
RFK Jr.’s stance on Covid vaccines for pregnant women is profoundly unethical
It
is squarely unethical to treat healthy pregnant women differently than
other groups that are similarly at elevated risk of serious Covid
illness, writes one bioethicist.
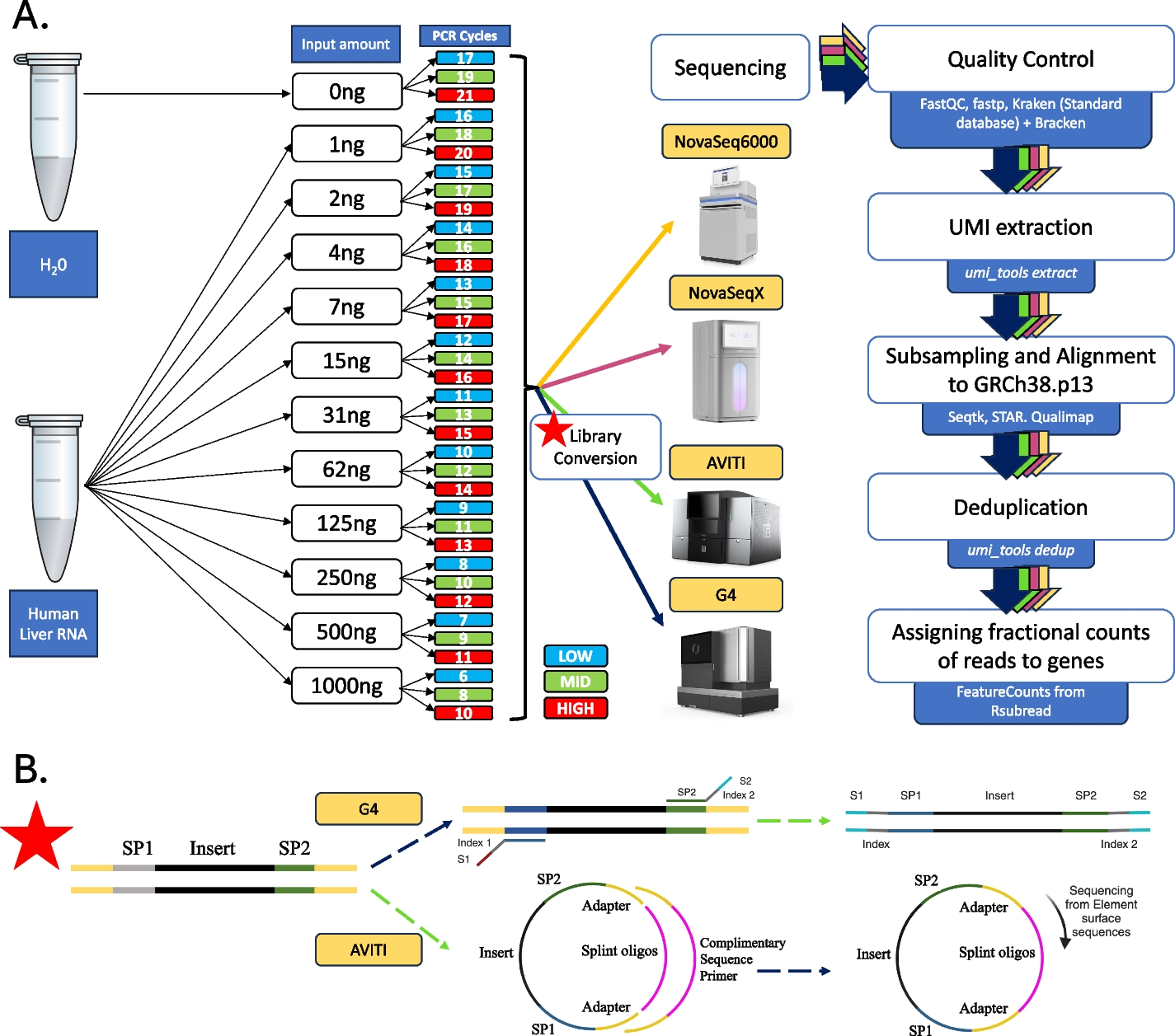
The impact of PCR duplication on RNAseq data generated using NovaSeq 6000, NovaSeq X, AVITI, and G4 sequencers - Genome Biology
Background
Transcriptome sequencing (RNA-seq) is a powerful technology for gene
expression profiling. Selection of optimal parameters for cDNA library
generation is crucial for acquisition of high-quality data. In this
study, we investigate the impact of the amount of RNA and the number of
PCR cycles used for sample amplification on the rate of PCR duplication
and, in consequence, on the RNA-seq data quality. Results For broader
applicability, we sequenced the data on four short-read sequencing
platforms: Illumina NovaSeq 6000, Illumina NovaSeq X, Element
Biosciences AVITI, and Singular Genomics G4. The native Illumina
libraries were converted for sequencing on AVITI and G4 to assess the
effect of library conversion, containing additional PCR cycles. We find
that the rate of PCR duplicates depends on the combined effect of RNA
input material and the number of PCR cycles used for amplification. For
input amounts lower than 125 ng, 34–96% of reads were discarded via
deduplication with the percentage increasing with lower input amount and
decreasing with increasing PCR cycles. The reduced read diversity for
low input amounts leads to fewer genes detected and increased noise in
expression counts. Conclusions Data generated with each of the four
sequencing platforms presents similar associations between starting
material amount and the number of PCR cycles on PCR duplicates, a
similar number of detected genes, and comparable gene expression
profiles.
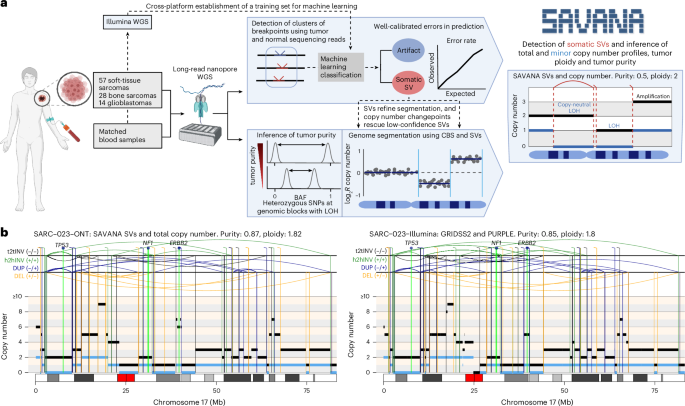
SAVANA: reliable analysis of somatic structural variants and copy number aberrations using long-read sequencing - Nature Methods
SAVANA
is a tool to detect somatic structural variants and copy number
aberrations using long-read sequencing data, offering high sensitivity,
specificity and compatibility with or without germline controls.
Epigenetic Clocks: New Types, New Promises, New Skepticism
Will birthdays go the
way of the Betamax and Blackberry? Our culture is always eager to move
away from old things toward new things and these days if you want to
know how old you are, the number of candles on your cake is just one
clue — and maybe not even the best clue.
Epigenetic clocks measure what’s happening inside you on a cellular
level and they might say you’re aging faster (or slower) than you
thought based on changes to your DNA.
Philanthropies rush to save measles surveillance network pushed to brink of collapse by U.S. cuts
The
Trump administration’s gutting of global aid is threatening to collapse
a network of laboratories responsible for global measles and rubella
surveillance

Stem cell therapy gains momentum in hearing loss care
As stem cell research gains momentum, researchers are looking at ways to use the therapy to treat hearing loss.























