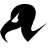Weekly Reading List: June 9, 2025

Scientists worry about possible publishing ban
HHS secretary Kennedy says the US might launch alternatives to leading medical journals
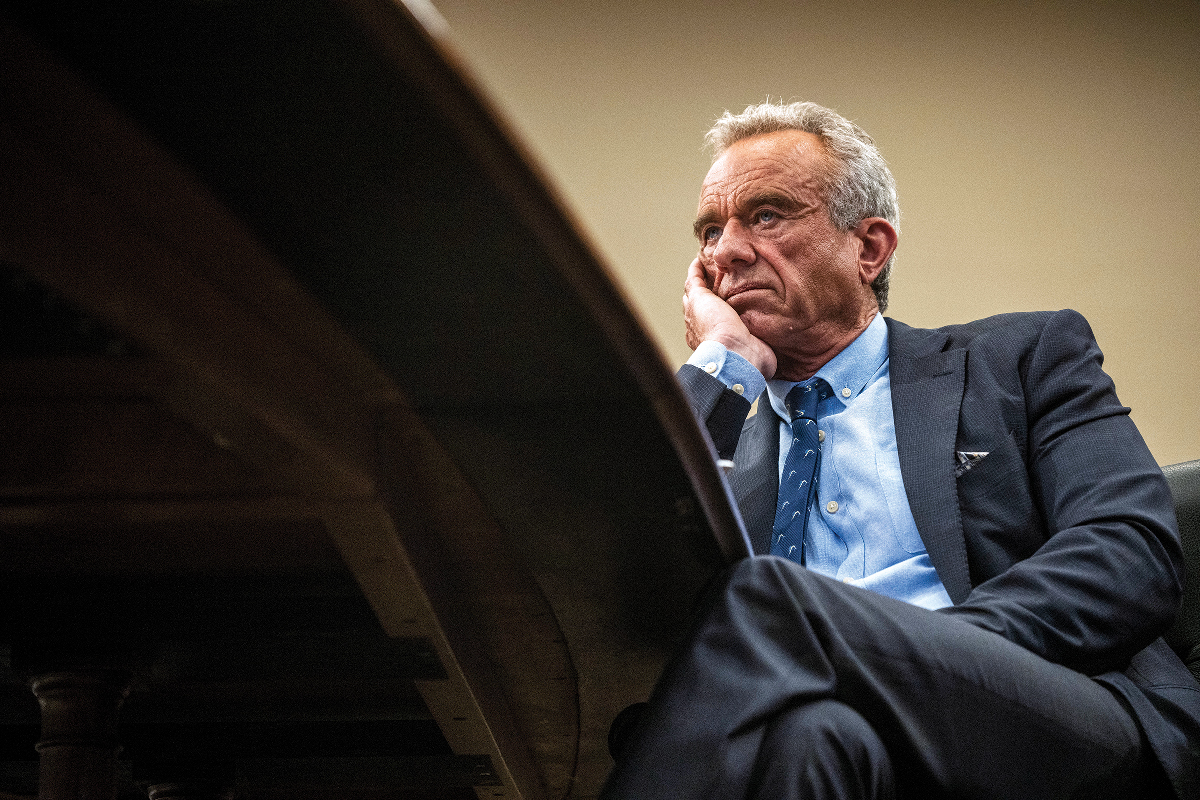

Efficient mRNA delivery to resting T cells to reverse HIV latency - Nature Communications
Resting
T cells are difficult to manipulate, and are a reservoir for latent
HIV. Here, the authors develop a lipid nanoparticle formulation with the
ability to transfect resting primary human T cells, enabling delivery
of mRNAs that result in reactivation of latent HIV. This could help
development of HIV cure strategies.
The pandemic generation: How Covid-19 lockdowns left a long-lasting mark on children
The
stress and isolation of the pandemic have left social and emotional
scars that are already being seen in children, but scientists also
predict there could be huge economic costs.

Skyrocketing mpox outbreak in Sierra Leone raises fears of wider spread
Boom in infections in the West African nation is driven by the same viral strain that caused a global outbreak in 2022.

Race, ethnicity don’t match genetic ancestry, according to a large U.S. study
Data from the All of Us program confirm what many geneticists have long promoted
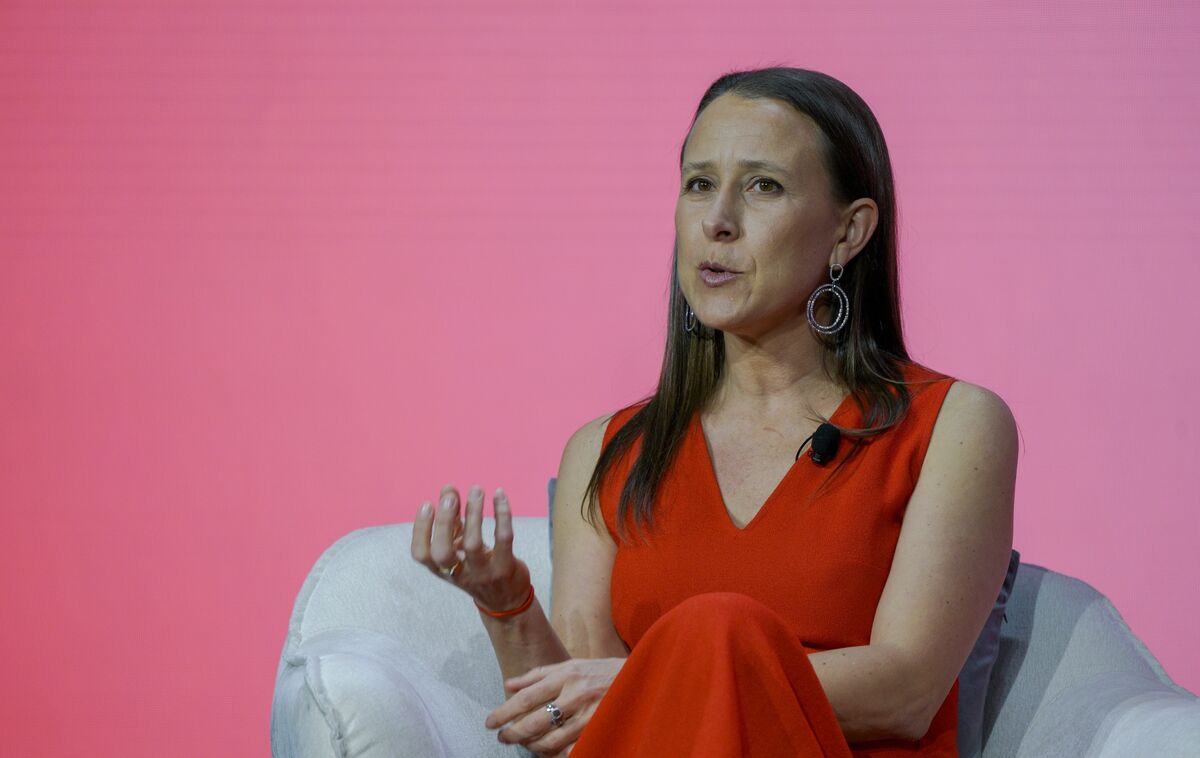
23andMe Sets New Auction With $305 Million New Bid From Ex-CEO
Bankrupt
genetic analysis company 23andMe will hold a second auction for its
cache of DNA data with an opening bid of $305 million from a group led
by the company’s former chief executive officer, Anne Wojcicki.

How We Pioneered Next Generation DNA Sequencing At Solexa – VII
Innovation is Aerobic

How We Pioneered Next Generation DNA Sequencing At Solexa – IX
Postscript

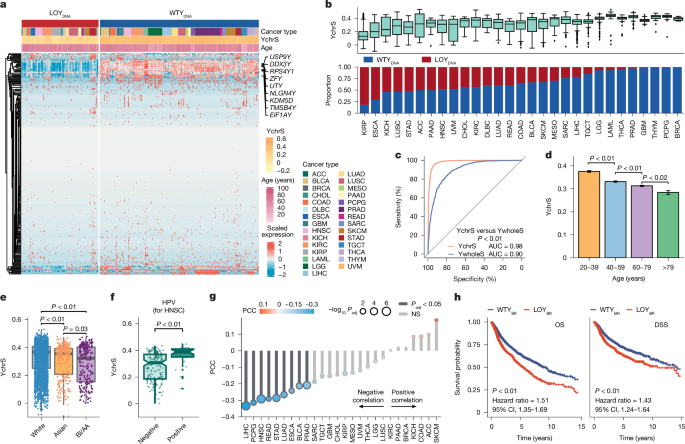
Concurrent loss of the Y chromosome in cancer and T cells impacts outcome - Nature
Comprehensive
pan-cancer analysis of loss of the Y chromosome (LOY) in benign and
malignant cells establishes a new model linking LOY in circulating and
tumour-infiltrating immune cells to LOY in malignant cells.
FDA’s AI tool, Elsa, is here. ‘The stupidest big fuss they ever made’
This is the web edition of STAT’s AI Prognosis, our subscriber-exclusive newsletter.
NIH indirect cost cuts will affect the economy and employment - Nature Human Behaviour
Nature Human Behaviour - NIH indirect cost cuts will affect the economy and employment
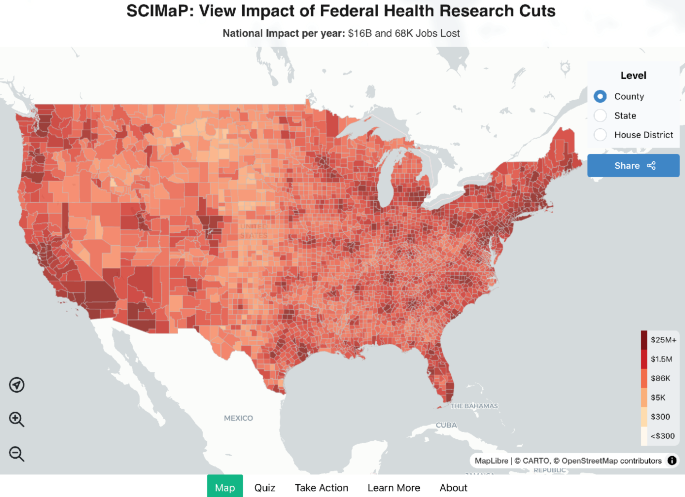
A National Lobotomy
Cutting
federal support for NIH and NSF is a national lobotomy that will
negatively affect our nation’s economy, education, and productivity.

Some signs of AI model collapse begin to reveal themselves
Opinion: Prediction: General-purpose AI could start getting worse

Genomic map of the functionally extinct northern white rhinoceros (Ceratotherium simum cottoni)
The northern white
rhinoceros (NWR; Ceratotherium simum cottoni) is functionally extinct,
with only two nonreproductive females remaining alive. Extraordinary
measures are underway to rescue this species, including using a
collection of NWR induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to generate
gametes for assisted reproduction technologies. Because of the critical
importance of genomic integrity in germ cells used for reproduction,
these approaches require extensive genomic analyses to exclude
aberrations that are acquired during culture of iPSCs.
Anti-ageing effects of popular supplement taurine challenged
Massive study finds limited connection between ageing and taurine levels in people, monkeys and mice.

At Columbia, dismay among chemical scientists
Some have already lost grants, while others fear for students and future funding

Alan Alda's Experiment: Helping Scientists Learn To Talk To The Rest Of Us
Alan Alda's father
wanted him to become a doctor, but it wasn't meant to be. "I failed
chemistry really disastrously ... " Alda says. "I really didn't want to
be a doctor; I wanted to be a writer and an actor."
FDA Abandons Its Defense of the LDT Rule, But is It Signaling an Increase in RUO Scrutiny?
At
midnight on Friday, May 30, 2025, the government’s deadline to notice
an appeal from the U.S. District Court for the Eastern District of
Texas’s decision vacating the LDT Rule lapsed without the…

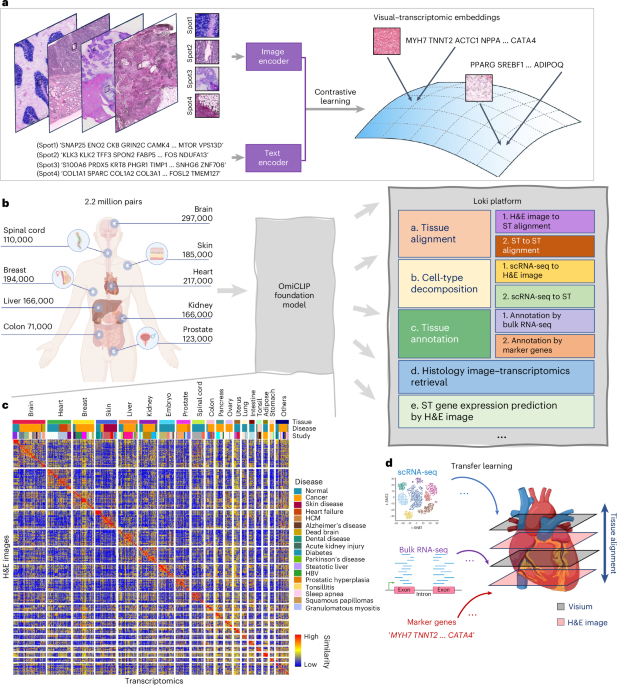
A visual–omics foundation model to bridge histopathology with spatial transcriptomics - Nature Methods
OmiCLIP
is a visual–omics foundation model that integrates histology and
spatial transcriptomics. The associated Loki platform offers accurate
and robust tools for alignment, annotation, cell-type decomposition and
spatial gene expression prediction.
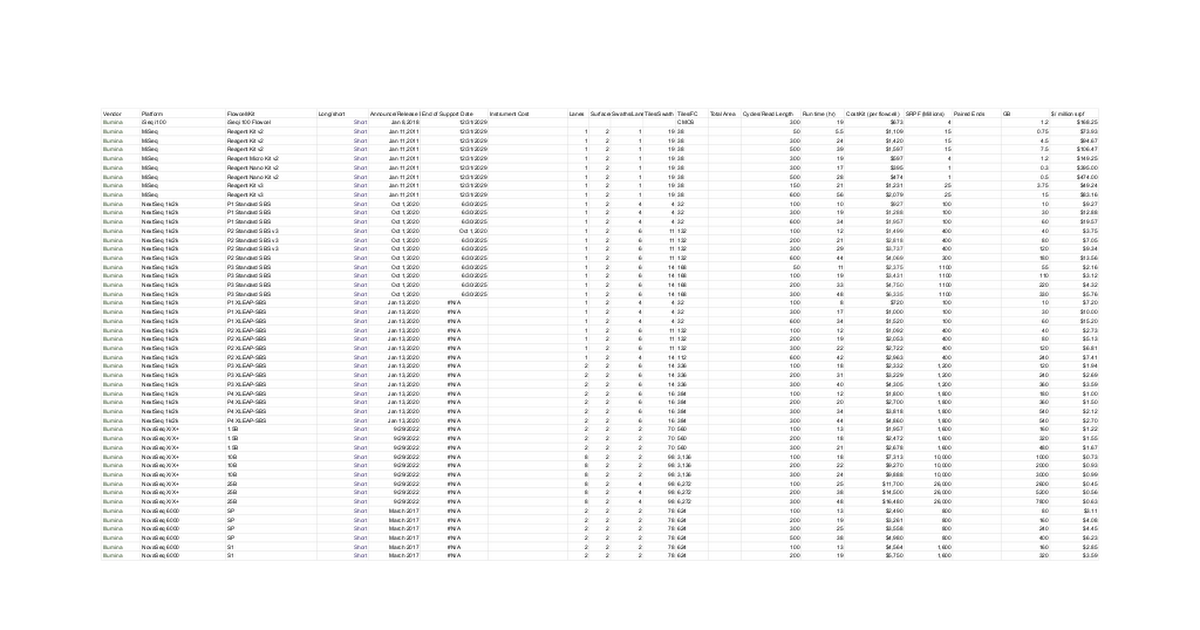
DNA Sequencers/Flowcells (On market)
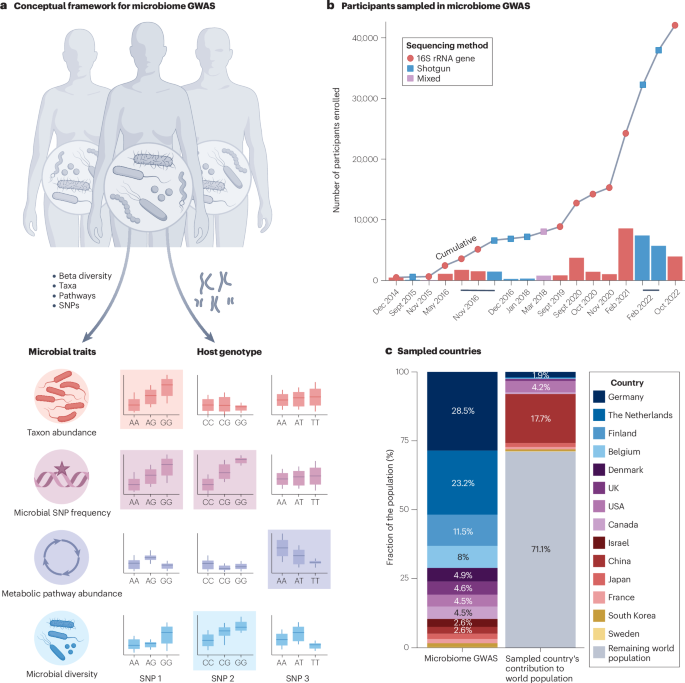
Genomics of host–microbiome interactions in humans - Nature Reviews Genetics
In
this Review, Ferretti et al. discuss advances in our understanding of
interactions between the human genome and the microbiome, including the
effects of the microbiome on host gene regulation.
Complete reference genome and
pangenome improve genome-wide detection and interpretation of DNA
methylation using sequencing and array data
The complete
telomere-to-telomere human genome assembly (T2T-CHM13) and the draft
human pangenome reference provide unique opportunities to refine DNA
methylation (DNAm) studies. Here, we find that T2T-CHM13 calls 7.4% more
CpGs genome wide compared to GRCh38 across four widely used short-read
DNAm profiling methods and improves the evaluation of probe
cross-reactivity and mismatch for Illumina DNAm arrays, yielding new and
more reproducible sets of unambiguous probes. The pangenome reference
further expands CpG calling by 4.5% in short-read sequencing data and
identifies cross-population and population-specific unambiguous probes
in DNAm arrays, owing to its improved representation of genetic
diversity.
Do you remember the Human Genome Project? I’m not sure the Trump administration wants you to
The NIH archives of the Human Genome Project could fall victim to Trump administration cuts, writes a former archivist.

GitHub - Shashi-Sekar/GeneChat: Multi-Modal LLM for Gene Function Prediction
Multi-Modal LLM for Gene Function Prediction. Contribute to Shashi-Sekar/GeneChat development by creating an account on GitHub.
Performance of deep-learning-based approaches to improve polygenic scores - Nature Communications
Polygenic
scores aim to capture genetic risk but may miss nonlinear genetic and
environmental interactions. Here, the authors show that neural networks
detect limited nonlinearity and do not outperform linear models,
highlighting constraints in current deep-learning approaches.
Focus on single gene effects limits discovery and interpretation of complex trait-associated variants
Standard
QTL mapping approaches consider variant effects on a single gene at a
time, despite abundant evidence for allelic pleiotropy, where a single
variant can affect multiple genes simultaneously. While allelic
pleiotropy describes variant effects on both local and distal genes or a
mixture of molecular effects on a single gene, here we specifically
investigate allelic expression “proxitropy”: where a single variant
influences the expression of multiple, neighboring genes. We introduce a
multi-gene eQTL mapping framework - cis-principal component expression
QTL (cis-pc eQTL or pcQTL) - to identify variants associated with shared
axes of expression variation across a cluster of neighboring genes. We
perform pcQTL mapping in 13 GTEx human tissues and discover novel loci
undetected by single-gene approaches. In total, we identify an average
of 1396 pcQTLs/tissue, 27% of which were not discovered by single-gene
methods. These novel pcQTL colocalized with an additional 142 GWAS
trait-associated variants and increased the number of colocalizations by
34% over single-gene QTL mapping. These findings highlight that moving
beyond single-gene-at-a-time approaches toward multi-gene methods can
offer a more comprehensive view of gene regulation and complex
trait-associated variation. ### Competing Interest Statement S.B.M is on
the scientific advisory board of MyOme, PhiTech and Valinor
Therapeutics. NIH, R01MH12524, U01AG072573, U01HG012069, T32HG000044

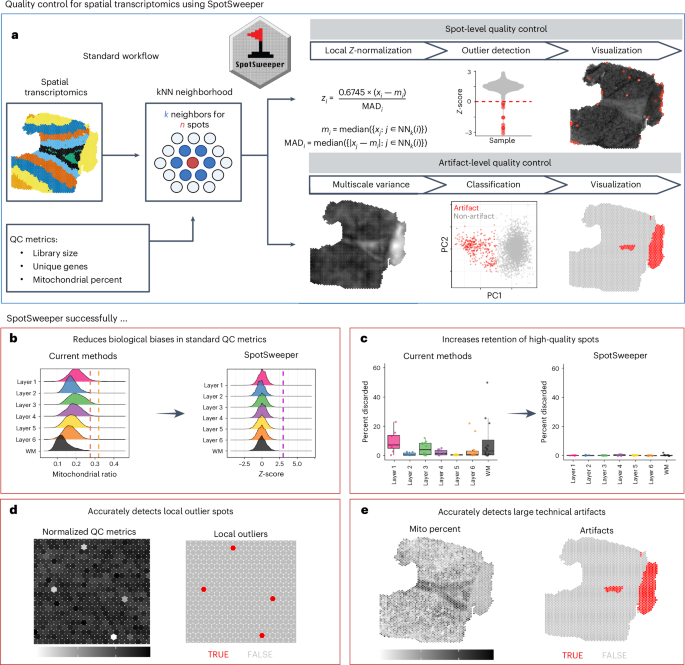
SpotSweeper: spatially aware quality control for spatial transcriptomics - Nature Methods
SpotSweeper
is a spatially aware method for quality control of spatially resolved
transcriptomics data that corrects for spatial confounding missed by
existing methods, including both local and regional artifacts, across
diverse technologies.